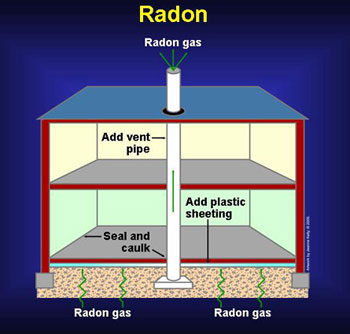
Ultra Violet Radiation comes from the sun, sunlamps, and tanning booths. It causes early aging of the skin and skin damage that can lead to skin cancer.
Also called UV Radiation, ultraviolet radiation consists of invisible rays that are part of the energy that comes from the sun. Ultraviolet radiation that reaches the Earth's surface is made up of two types of rays, called UVA and UVB. Ultraviolet radiation also comes from sun lamps and tanning beds. Research indicates that ultraviolet radiation causes skin damage, premature aging, melanoma, and other types of skin cancer, as well as problems with the eyes and the immune system.