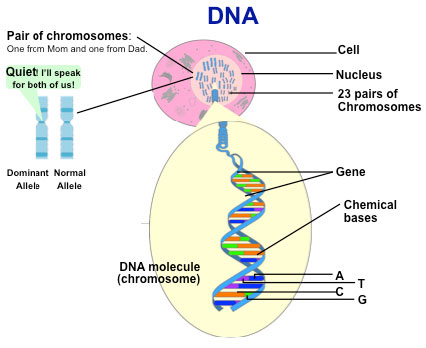
Genes
- Genes are made up of DNA.
- Every cell in our body contains the same genes but different genes are active in
different cell types, tissues and organs, producing the necessary specific proteins.
- Some genes are turned on and others are turned off.
- Each chromosome contains many genes but each has a different number and type.
- Genes instruct our cells how to function by making mRNA and then proteins by reading
the DNA blueprint.
Chromosomes
Chromosomes are large DNA molecules composed of two chemical strands that are
twisted around each other to form a "double helix." We each have 23 pairs of
chromosomes - 22 pairs are identical or autosomal and the 23rd pair is a set of sex
chromosomes (XX=female / XY=male).
RNA
RNA is one of the two types of nucleic acids found in all cells. RNA uses a different
base pairing rule than DNA:
- A matches only with U (uracil) instead of T
- C still matches with G.
In the cell, RNA is made from DNA (the other type of nucleic acid), and proteins are
made from RNA.
Proteins
Proteins are assembled from amino acids using information encoded in genes. Proteins
are the basis of body structures such as skin and hair and of substances such as
enzymes, cytokines, and antibodies.
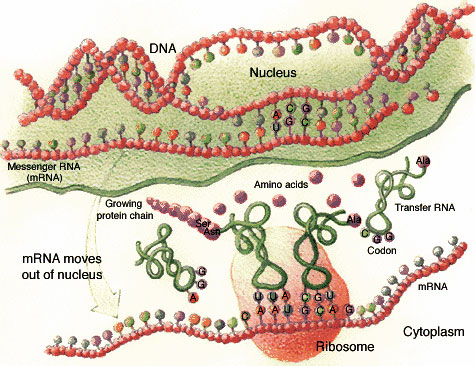
Genes to mRNA to Proteins - Explanation of the image below
When a gene expresses itself, it "switches on" to produce a protein. The gene does so by
first directing the synthesis of an intermediary molecule called messenger ribonucleic
acid (mRNA).
|
Image courtesy of 1996 To Know Ourselves, The U.S.Department of Energy and the Human Genome Project |
Genome
Every organism, including humans, has a genome that contains all of the biological
information needed to build and maintain a living example of that organism.
The biological information contained in a genome is encoded in its deoxyribonucleic acid
(DNA) and is divided into discrete units called genes. Genes code for proteins that attach
to the genome at the appropriate positions and switch on a series of reactions called gene
expression.
The "Central Dogma"
"DNA makes RNA, RNA makes protein, and proteins make us." Francis Crick
 |
|
All individuals are 99.9 percent the same with respect to their DNA sequence. |
| Image courtesy of Genome Management Information System, Oak Ridge National Laboratory |
We have provided background information about cells, the cell cycle and genetic structure
to help you understand the normal process of each of these components. We have a little
more basic information to provide and then we will move to the disruption of the normal
process that leads to cancer.